Monitoring Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) Clusters with Splunk Enterprise and Splunk Cloud
March 15, 2018[UPDATE (2018-06-15)] Base on Amazon ECS Adds Daemon Scheduling we updated our blog post to show how you can schedule our collector on ECS by using new Daemon Scheduling.
[UPDATE (2018-10-15)] Updated to Monitoring Docker v5.2
Amazon EC2 Container Service (ECS) is a highly scalable, high performance container management service that supports Docker containers and allows you to easily run applications on a managed cluster of Amazon EC2 instances.
Because ECS is running Docker as a Container Engine, our solution for Monitoring Docker works out of the box with it as well.
In our example we used ECS and Splunk deployed at the same Region and the same VPC. But there is no special requirements on your Splunk Enterprise deployment. You can also use Splunk Cloud with our solution. The only requirement is to give EKS cluster access to the Splunk HTTP Event Collector endpoint, which is usually deployed on port 8088.
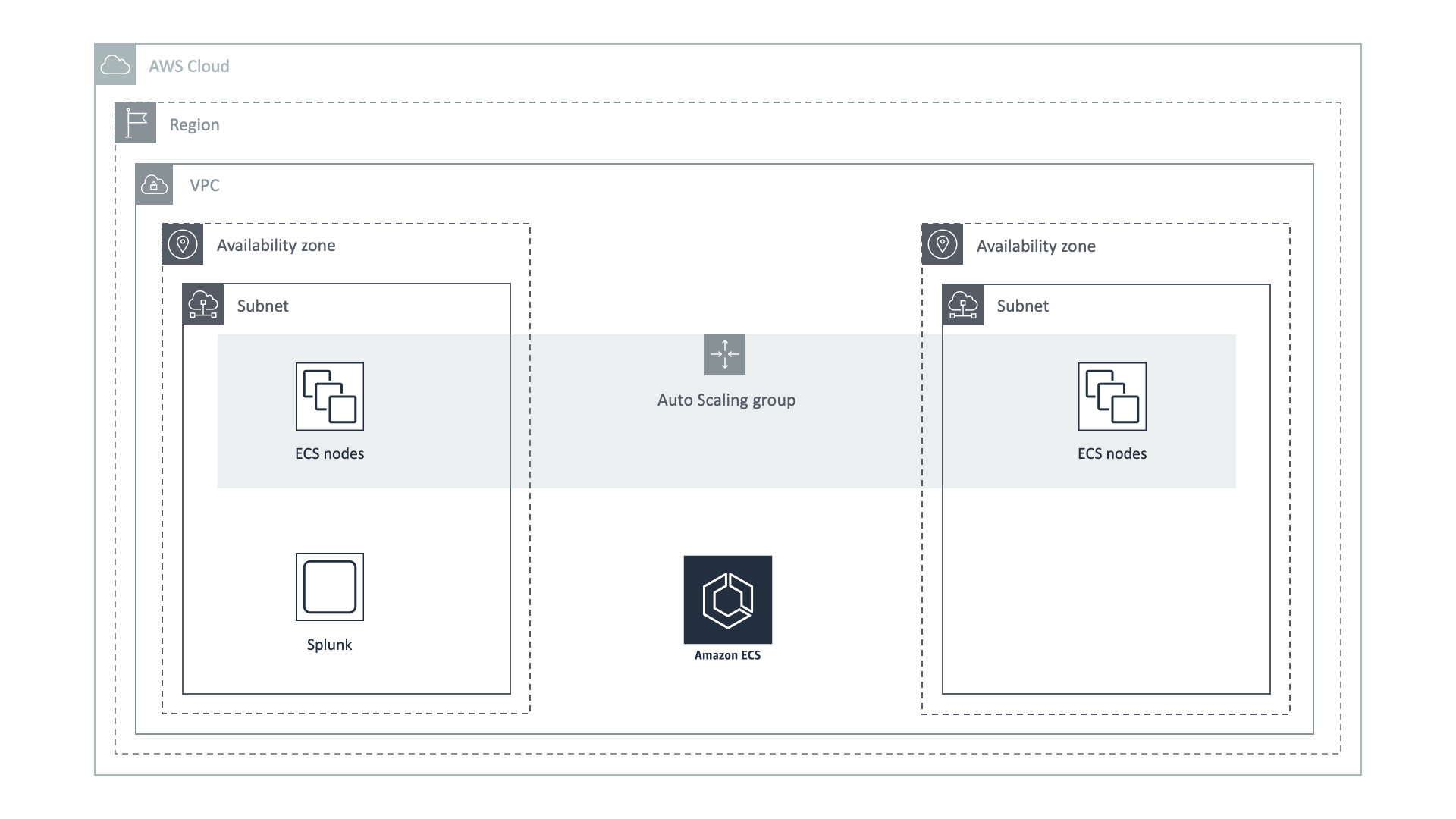
We expect that you already finished Splunk configuration from our manual Monitoring Docker Installation, installed our application Monitoring OpenShift and enabled HTTP Event Collector in your Splunk environment.
At first, you need to create a new Task Definition
At the very bottom, you can find a Configure JSON button
Use following template to create a Task Definition, where at a minimum you need to set URL for your HTTP Event Collector and specify your HTTP Event Collector Token and include license key (request an evaluation license key with this automated form). You can also revisit Memory and CPU limits, specific for your load, and you can adjust that later.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 | { "containerDefinitions": [ { "name": "collectorfordocker", "image": "outcoldsolutions/collectorfordocker:5.22.422", "memory": "256", "cpu": "256", "essential": true, "portMappings": [], "environment": [ { "name": "COLLECTOR__SPLUNK_URL", "value": "output.splunk__url=https://hec.example.com:8088/services/collector/event/1.0" }, { "name": "COLLECTOR__SPLUNK_TOKEN", "value": "output.splunk__token=B5A79AAD-D822-46CC-80D1-819F80D7BFB0" }, { "name": "COLLECTOR__SPLUNK_INSECURE", "value": "output.splunk__insecure=true" }, { "name": "COLLECTOR__ACCEPTLICENSE", "value": "general__acceptLicense=true" }, { "name": "COLLECTOR__LICENSE", "value": "general__license=..." }, { "name": "COLLECTOR__EC2_INSTANCE_ID", "value": "general__ec2Metadata.ec2_instance_id=/latest/meta-data/instance-id" }, { "name": "COLLECTOR__EC2_INSTANCE_TYPE", "value": "general__ec2Metadata.ec2_instance_type=/latest/meta-data/instance-type" } ], "mountPoints": [ { "sourceVolume": "cgroup", "containerPath": "/rootfs/sys/fs/cgroup", "readOnly": true }, { "sourceVolume": "proc", "containerPath": "/rootfs/proc", "readOnly": true }, { "sourceVolume": "var_log", "containerPath": "/rootfs/var/log", "readOnly": true }, { "sourceVolume": "var_lib_docker_containers", "containerPath": "/rootfs/var/lib/docker/", "readOnly": true }, { "sourceVolume": "docker_socket", "containerPath": "/rootfs/var/run/docker.sock", "readOnly": true }, { "sourceVolume": "collector_data", "containerPath": "/data", "readOnly": false } ], "volumesFrom": null, "hostname": null, "user": null, "workingDirectory": null, "privileged": true, "readonlyRootFilesystem": true, "extraHosts": null, "logConfiguration": null, "ulimits": null, "dockerLabels": null, "logConfiguration": { "logDriver": "json-file", "options": { "max-size": "1m", "max-file": "3" } } } ], "volumes": [ { "name": "cgroup", "host": { "sourcePath": "/cgroup" } }, { "name": "proc", "host": { "sourcePath": "/proc" } }, { "name": "var_log", "host": { "sourcePath": "/var/log" } }, { "name": "var_lib_docker_containers", "host": { "sourcePath": "/var/lib/docker/" } }, { "name": "docker_socket", "host": { "sourcePath": "/var/run/docker.sock" } }, { "name": "collector_data", "host": { "sourcePath": "/var/lib/collectorfordocker/data/" } } ], "networkMode": null, "memory": "256", "cpu": "0.5 vcpu", "placementConstraints": [], "family": "collectorfordocker", "taskRoleArn": "" } |
After saving it, you can use this Task Definition on your ECS clusters.
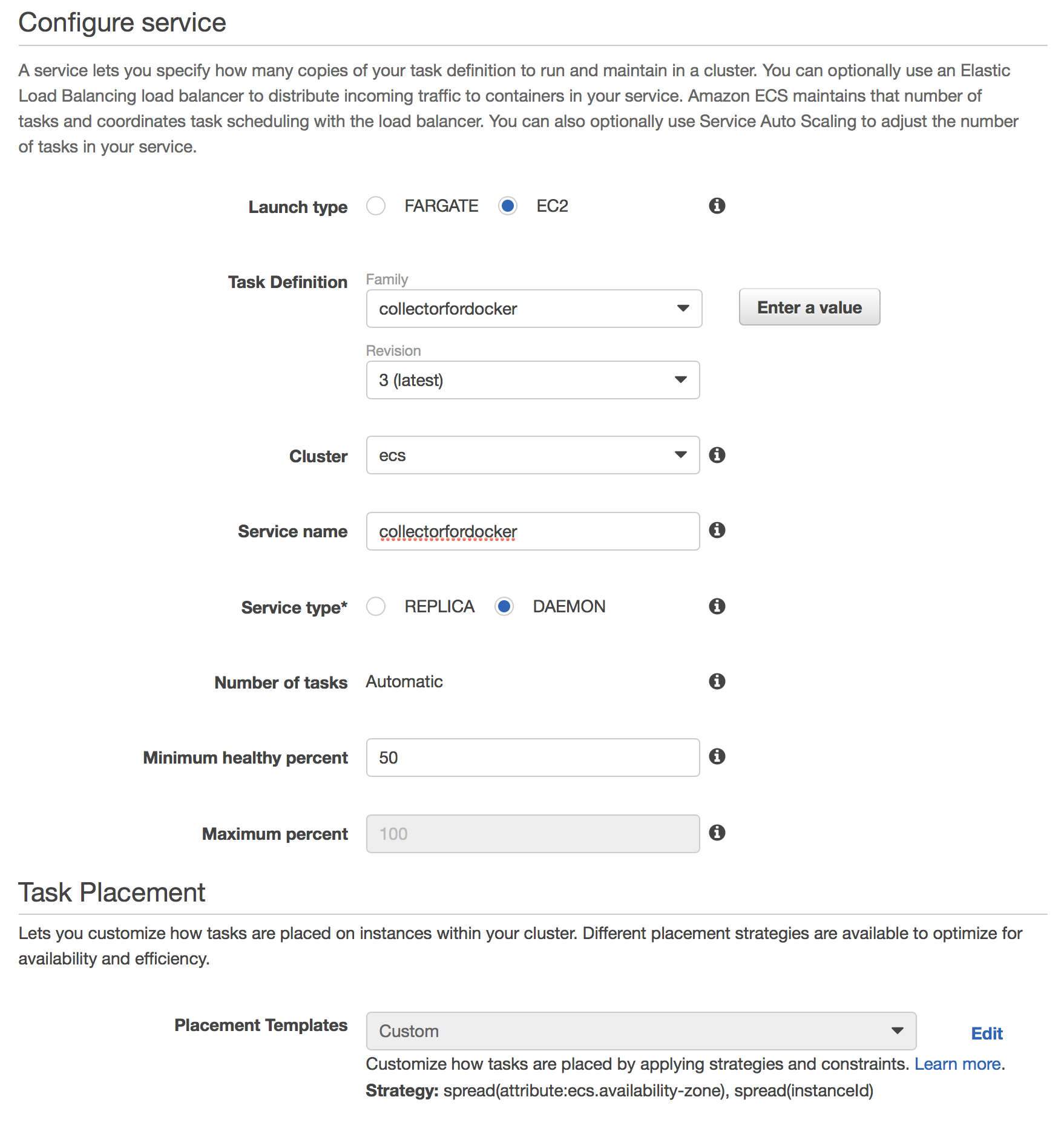
Next step is to schedule this Task on every host we have. Open your cluster and go to the Services tab
Create a new service with following configuration:
- Launch type - EC2
- Task Definition - choose just created task definition
collectorfordocker - Cluster - the name of your ECS cluster.
- Service name -
collectorfordocker - [UPDATE (2018-06-15)] Service Type -
DAEMON. - Minimum healthy percent - keep defaults (we aren't going to use them)
- On the second step choose: Load balancer type - None
- On the third step: Service Auto Scaling - Do not adjust the service’s desired count
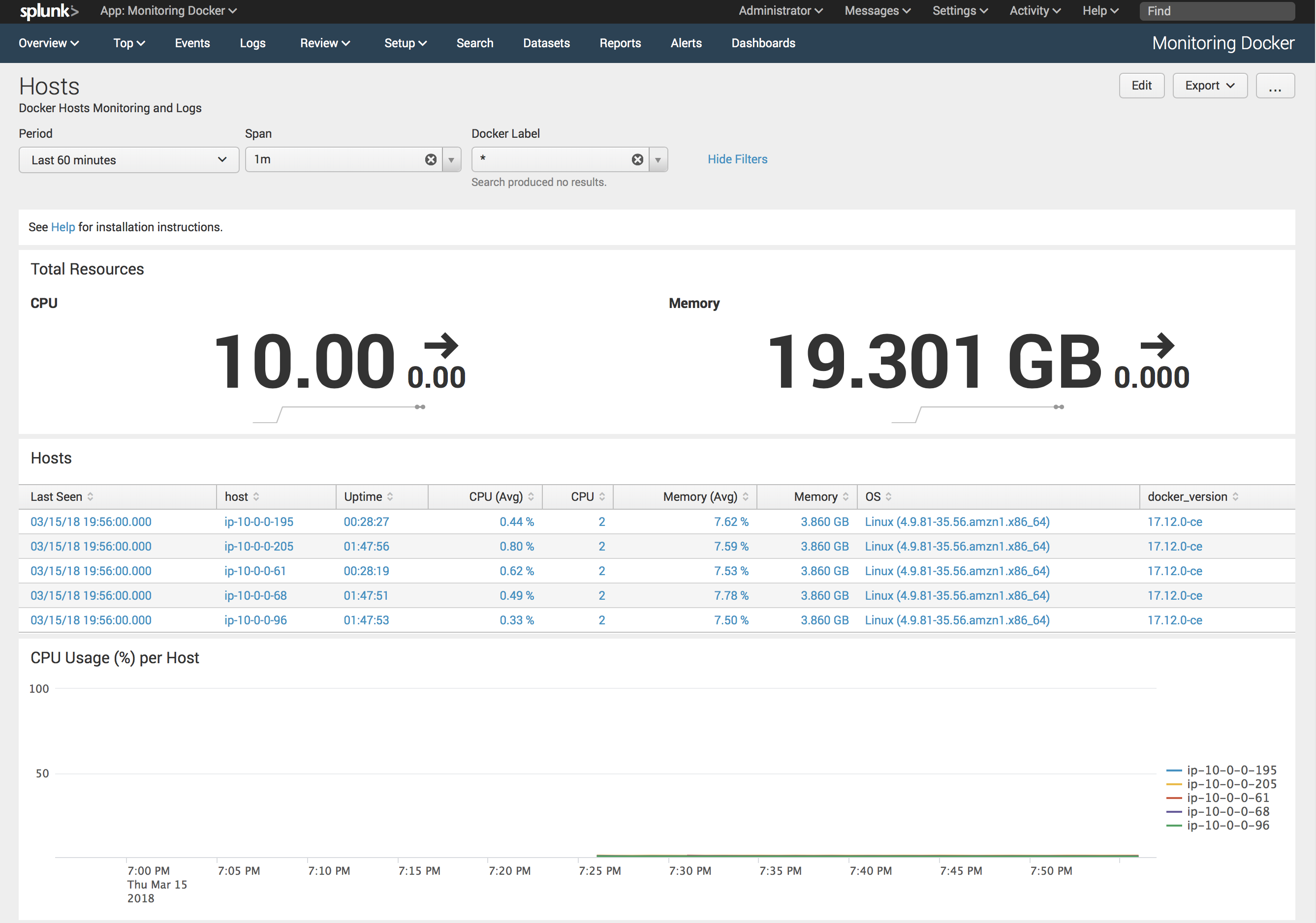
After creating the service give it a minute to download an image and setup our collector. If everything works as expected, you should see data in Monitoring Docker application.
Known issues
- By default collector picks up docker daemon logs from
/rootfs/var/log/docker, you need to update macromacro_docker_host_logs_dockerand change it to
(`macro_docker_host_logs` AND source="*var/log/docker*")



