Splunk Indexes
By default, collectorforkubernetes forwards all events to the default index specified for the HTTP Event Collector Token.
Every HTTP Event Collector Token has a list of indexes where this specific Token can write data. One of the indexes
from this list is also used as the default index when the sender of the data does not specify a target index.
The application assumes that you are writing data to indexes that are searchable by default by your Splunk role.
For example, the main index is searchable by default.
If you use a different index that isn’t searchable by default by your Splunk role, you would not see data on the dashboards.
To fix this, you can include this index in the Indexes searched by default for your role under Settings - Access Control
- Roles
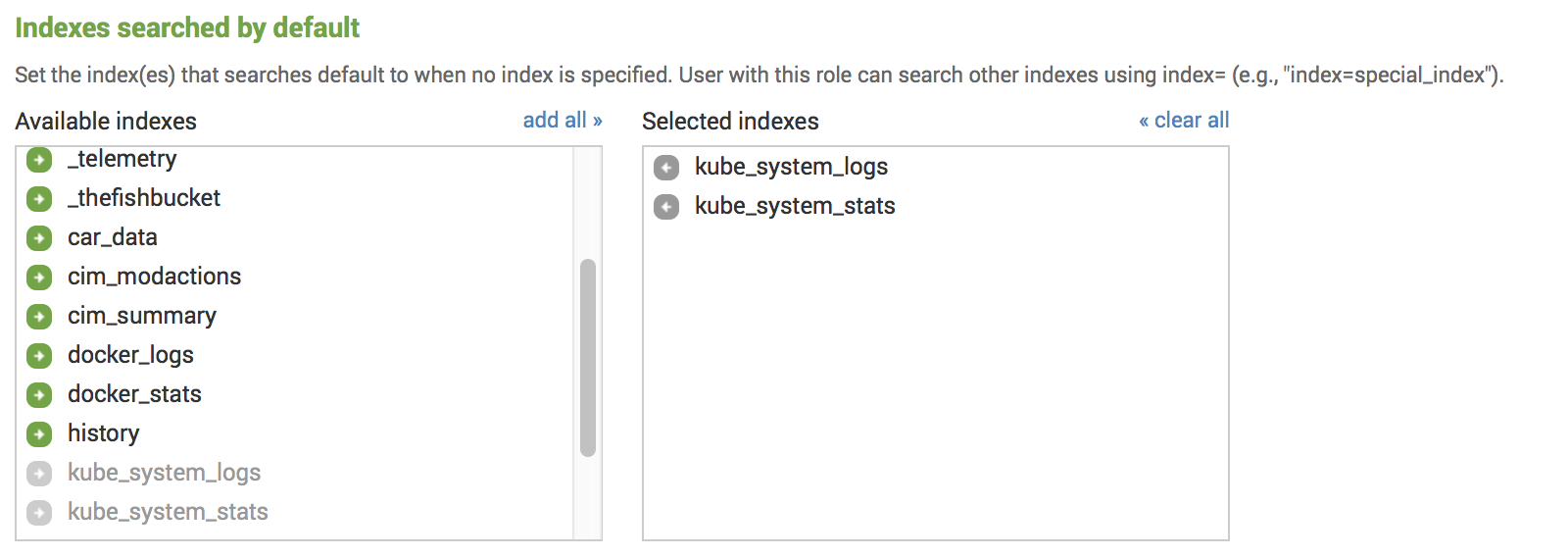
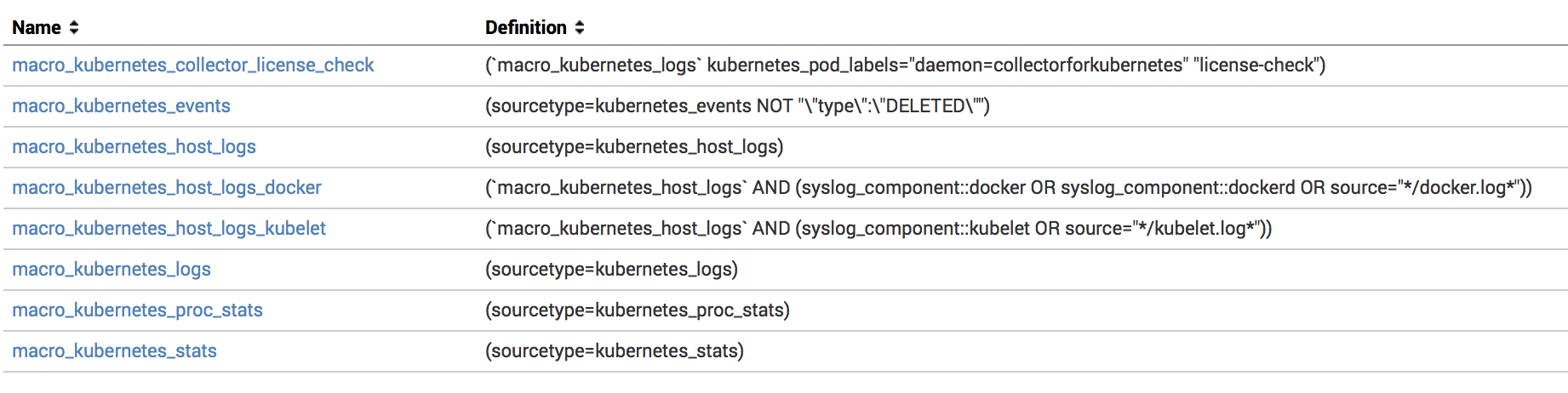
Or you can change the Search Macros we use in the application and include a list of indexes you use for Monitoring Kubernetes events. You can find search macros in the Splunk Web UI under Settings - Advanced search
- Search macros (or by overriding
$SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps/monitoringkubernetes/default/macros.confwith$SPLUNK_HOME/etc/apps/monitoringkubernetes/local/macros.conf).
Starting from version 5.10, we include a base macro macro_kubernetes_base where you can include the list of indexes only
once, and all other macros will inherit this configuration.
macro_kubernetes_base = (index=kubernetes_stats OR index=kubernetes_logs)
If you want to have more precise configuration, you can modify specific macros.
macro_kubernetes_stats = (index=kube_system_stats sourcetype=kubernetes_stats)
You only need to update the following macros:
macro_kubernetes_events- all the kubernetes events.macro_kubernetes_host_logs- host logs.macro_kubernetes_logs- container logs.macro_kubernetes_proc_stats- proc metrics.macro_kubernetes_net_stats- network metrics.macro_kubernetes_net_socket_table- network socket tables.macro_kubernetes_stats- system and container metrics.macro_kubernetes_mount_stats- container runtime storage usage metrics.macro_kubernetes_prometheus_metrics- metrics from prometheus format
Using dedicated indexes for different types of data
Considering the application access patterns and the content of the events, we recommend splitting logs and metrics
and using dedicated indexes. For example, kube_system_logs for events, container and host logs; kube_system_stats for
proc and system metrics; and kube_prometheus for Prometheus metrics.
You can also specify a dedicated index for every type of data that collectord forwards.
Using dedicated indexes also allows you to specify different retention policies for logs and metrics.
You can do that by using the Configuration Reference file and setting the values of the indexes you want to use as the destination.
data:
collector.conf: |
...
[input.system_stats]
...
# specify Splunk index
index =
...
[input.proc_stats]
...
# specify Splunk index
index =
...
[input.net_stats]
...
# specify Splunk index
index =
...
[input.net_socket_table]
...
# specify Splunk index
index =
...
[input.mount_stats]
...
# specify Splunk index
index =
...
[input.files]
...
# specify Splunk index
index =
...
[input.files::syslog]
...
# specify Splunk index
index =
...
[input.files::logs]
...
# specify Splunk index
index =
...
[input.kubernetes_events]
...
# specify Splunk index
index =
...
Configuring dedicated indexes, source and sourcetype for Namespaces
You can also override targeted indexes for namespaces in Kubernetes. The Collectord watches for annotations on namespaces,
workloads, and pods. For example, if you want to specify that you want to index all container logs, metrics, and events in the specific
namespace namespace1 to index kubernetes_namespace1, you can annotate this namespace with
kubectl annotate namespaces namespace1 \
collectord.io/index=kubernetes_namespace1
You can learn more about available annotations in Annotations
Links
- Installation
- Start monitoring your Kubernetes environments in under 10 minutes.
- Automatically forward host, container and application logs.
- Test our solution with the embedded 30-day evaluation license.
- Collectord Configuration
- Collectord configuration reference.
- Annotations
- Changing index, source, sourcetype for namespaces, workloads and pods.
- Forwarding application logs.
- Multi-line container logs.
- Fields extraction for application and container logs (including timestamp extractions).
- Hiding sensitive data, stripping terminal escape codes and colors.
- Forwarding Prometheus metrics from Pods.
- Audit Logs
- Configure audit logs.
- Forwarding audit logs.
- Prometheus metrics
- Collect metrics from control plane (etcd cluster, API server, kubelet, scheduler, controller).
- Configure the collectord to forward metrics from the services in Prometheus format.
- Configuring Splunk Indexes
- Using non-default HTTP Event Collector index.
- Configure the Splunk application to use indexes that are not searchable by default.
- Splunk fields extraction for container logs
- Configure search-time field extractions for container logs.
- Container logs source pattern.
- Configurations for Splunk HTTP Event Collector
- Configure multiple HTTP Event Collector endpoints for Load Balancing and Fail-overs.
- Secure HTTP Event Collector endpoint.
- Configure the Proxy for HTTP Event Collector endpoint.
- Monitoring multiple clusters
- Learn how to monitor multiple clusters.
- Learn how to set up ACL in Splunk.
- Streaming Kubernetes Objects from the API Server
- Learn how to stream all changes from the Kubernetes API Server.
- Stream changes and objects from Kubernetes API Server, including Pods, Deployments or ConfigMaps.
- License Server
- Learn how to configure a remote License URL for Collectord.
- Monitoring GPU
- Alerts
- Troubleshooting
- Release History
- Upgrade instructions
- Security
- FAQ and the common questions
- License agreement
- Pricing
- Contact


